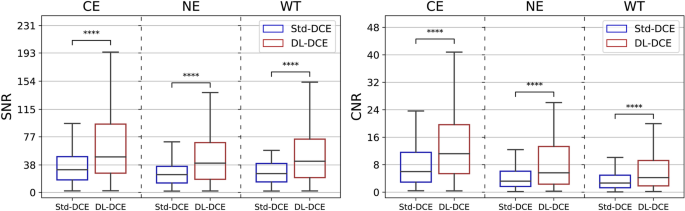
A cohort of 306 patients (mean age 53, 182 men) was analyzed for glioma characteristics, with WHO grade IV tumors predominating (72.9%). Molecular markers included IDH mutations (23.9%) and MGMT methylation (54.9%). Imaging studies demonstrated that deep learning-enhanced dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DL-DCE) significantly improved signal-to-noise (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratios (CNR) compared to standard DCE. DL-DCE also provided higher resolution images, enhancing tumor detail visibility. Diagnostic performance of pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters from DL-DCE was comparable to standard DCE, indicating its efficacy in differentiating tumor grades and IDH mutation status while improving reproducibility of arterial input function parameters.